Listen here to a Chrome AI-generated podcast type playback of the author’s article
Of all new technologies being developed, I can see three main ones that will dominate the food and agriculture (and most other sectors as well) scene in the years to come. As usual, I will not make a catalogue of technologies, companies or investment amounts. If you are interested, just ask any AI to produce a full report and you will get it in less than a minute. This is not what really matters. What matters is which technologies will get traction, which ones will be adopted and which ones will actually solve problems (see my previous post). The three areas of interest I have in mind are: artificial intelligence, robotics and gene technologies, and I will add a bonus fourth category at the end of the article. The latter is often overlooked, yet so important.
Artificial intelligence
Well, this one is not really original but AI is here. It is evolving and it is here to stay. It will bring many changes. Some will be good, others maybe not so much, but we are going to have to live with it. So, I will not be listing all the areas where AI will be used. Once again, use AI to give a full report. You can also do a search on this website to find all my articles about AI or look at my YouTube playlist about AI, too.
Instead, let’s review areas that are important to improve. AI was, perhaps still is, the missing link in digital food and agriculture. In my first book, published in 2010, I was already presenting the possibilities of having farming equipment units that would interact together. I foresaw this age of automation as being about building a nervous system. Until recently, the nervous system was still the human operator’s, because the previous age of mechanization was about giving the operator additional muscle, mostly in the form of mechanical horse power. It was replacing the legs and arms, if you wish. The digital age is giving the operator additional information processing abilities, and changing the relative functions of human and machines completely. All the data-collecting devices, such as drones, sensors, satellites and so on, would be extensions of senses. They can see, they can hear, they can smell, they can “feel” and be sure they can taste, too. But the one thing was missing with these devices, even from an IoT perspective were the synapses. That is what AI is. It makes data and information flow back and forth between all the devices, and the operator. It all sounds exciting, indeed. To quote the late French neurobiologist Henri Laborit, the purpose of a nervous system is not to think, it is there to act. I believe this is quite true for AI, too.
Yet, let’s not forget one thing: AI is not intelligent as such. It follows a mechanical structure. It looks like intelligence because it is so fast, actually faster than a human being, that it seems “alive”. That is a mistake we should not make. At least today. Let’s use AI for what it is today: an amazing assistant. As an assistant, it will do wonders. Like a speaker said in a presentation I was attending earlier this year: “AI is like having Einstein tied up in your basement”. That is quite a good comparison. The speaker in question is Steve Lerch. If you need someone to present you practical aspects of AI in an enticing manner and how it will help you add value to you customers, he is the person to have. The key is indeed to add value. It benefits your customers, and as a result it benefits you, too. To get there, it is necessary to know what to do with AI. This is where we need to move further.
First of all, proper training of operators is essential. I always say that new technologies and new tools need to come with a user’s manual. Of course, it can be fun to experiment to try to find out what you can do with the new toy, but that can be rather time consuming and the costs of mistakes along the way can end up being rather high. A well-prepared and well-structured training is an absolute requirement. Not only will it speed up the learning process but the quality of the training is where you can increase the desire to adopt and use the new technology. Playing with the toy is fun but just as it is always the case with toys, boredom or frustration happen fast and the toy is abandoned just a few days after Christmas, if you see what I mean.
Other area of improvement is the user friendliness. Systems like ChatGPT require prompting, and that part can be where the difficulties arise. Prompting still is challenging for many users and that can lead to frustration. Prompting needs to be more like instructions the user would ask another person (the assistant feel). And just like a human assistant, AI needs to ask questions if the instructions are too vague or unclear. Interactive is the key for an effective AI assistant, and for good results. It should be voice-activated and not just a typing exercise, people are less comfortable with the latter. Further, routine AI activities should be shaped as a menu with just buttons to push. Only then, it will become attractive.
A third area of work that is needed for AI is trust. It is a powerful tool and perhaps a little too much so. It can serve for good but it can also serve to mislead, deceive, destabilize or for criminal activities. AI needs to support critical thinking, which of course requires that users dispose of some themselves.
Beyond those issues, a number of other challenges will arise from the use of AI. One of them is to sort out who owns the data, who can use it and who cannot, or just even who can access the data and who cannot. Another challenge, which I mentioned above is crime. What happens is someone hacks the data and either takes it hostage, deletes it or even alters it? What would happen if food producers are suddenly unable to make decisions or even perform any work because of a malafide intrusion? We need to think quite seriously about this because the consequences could be rather devastating. I wish I heard more about the issue of criminal interference with AI than I do. Another, major, issue to address for the future is the current levels of energy and water use that AI requires. Can we afford AI altogether, or will it have to be “rationed”? What will be its impact on the environment and essential resources and what is the plan forward? Do we want some eccentric billionaires to own and run nuclear plants for their own AI platforms? A study from the University of Bonn, Germany had shown that all the data collected and used for crop productions and all the stakeholders of the value chain were stored by three companies: Microsoft, Google and Amazon. This shows the potential vulnerability and dependence of the entire food chain. How will we deal with that, too?
In the end, let’s not forget that technologies are not living creatures, although some like to think so or wish they were. Technologies are here to serve humans. We need a clear purpose, show some serious leadership about technology and not forget that competence and critical thinking will never be liabilities. They are the assets that will feed success.
Robotics
AI is the “backbone” of the new nervous system. It is part of an evolution, even though it is referred to as a revolution. Just like in biological evolution, any change, any mutation also brings a modification of the organism. The muscle I was mentioning earlier will just change. It is a “natural” consequence. This new nervous system is going to come along with the apparitions of new “organisms”. From that perspective, it is obvious that robotics are a natural extension of AI. We are starting to see this already. The recent plans of Amazon to eliminate 75% of its workforce by 2033, meaning elimination 600,000 US jobs show that AI and robotics will affect very strongly how businesses are run. There is no doubt in my mind that food and agriculture will also use more and more robots in the future, thanks to AI.
For agriculture, it might be as much of a new business model as it will be about the necessity to replace an increasingly difficult to find workforce. The causes may be many. Season work relies a lot on immigration and policies are making this more difficult. The number of farmers that are going to retire within a decade is actually rather scary and someone -or something- is going to have to do the job to feed the population.
So, how will robotics fit in? We can look at it from different angles. First, an improving AI will make robots more efficient and more cost-effective than now. The cost of robots and their payback time have been a disadvantage for the adoption of robotics in many areas of food and agriculture. If the economics change, expect to see the sector of robotics to make some serious progress. Secondly, the Amazon “effect” of going AI and robots will stimulate other sectors to look at their respective futures. Assuming that Amazon is successful, it will serve as examples in other industries. You can count on that. Thirdly, and also thanks to AI, the design of robots is going to change and I expect that future robots will be more nimble and easier to operate, and at a lower cost, too.
Gene technologies
Gene technologies certainly offer very interesting possibilities but the perception from the general public can be difficult. Genes are a sensitive topic and it does not take much to have fear blurry the conversation. Most of it has to do with the early beginnings of genetically modified organisms (GMO), in particular transferring a gene from one species to another. It did not need much to have GMOs associated with the idea of Frankenstein. In the food sector, the concept of Frankenfoods was born. Then came the Roundup-ready crops and the Bt-resistant crops which became major issues and still are today. The problem was not just about technical aspects of GMOs. The main player, Monsanto, just happened to be a terrible ambassador for genetic engineering. There is no need to pretend the contrary.
Anyway. the world has moved on, and so has genetic engineering. Just like I said about AI, if you want a catalogue of applications, just ask AI to provide you with a full report. Here I just want to browse through the scope of possible applications.
Since the beginning of selection of plants and animals by farmers, the focus was always to select the best performing individuals in a particular context. With biology, everything is relative. Some varieties or breeds may do well in certain environmental conditions and poorly in others. That was true in the early days of genetics and it still is true today.
Genetics are still a key part of selection and development of better plants and animals, as well as many other forms of life, such as microorganisms, but genetics is only half the equation. They are about genetic potential. The trick is to work in conditions that allow that potential to express itself to its maximum, if possible. Of course, there are many factors that can influence the outcome. Sometimes, conditions are positive, sometimes they are negative. Today, the challenge is also to at least minimize the impact of negative conditions so that the performance still stays acceptable even if Nature throws sticks in the farmers’ spokes, so to speak.
This is where gene technologies can help. They can help avoiding the expression of unfavorable genes, or allow some genes to express themselves against adverse conditions. It is what gene editing is about. There are many areas of work. Just think at the possibility of having plants that are more rustic to face difficult growing conditions such has drought or heat. It can be the possibility of having genes that offer resistance to diseases. This not just about financial aspects. It is also about animal welfare, as sick animals suffer. It is also about the environment as all yield losses from crops or sick animals are an inefficient use of resources.
For instance, the recent development of the PRRS-resistant pig (Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome), a disease that has serious economic and animal welfare impact is interesting. The gene-edited pig production has now been authorized by the US FDA. Of course, such a novelty meets resistance and criticism. That is the way change goes. Considering the risk of diseases, as I was mentioning them in a previous post, any progress that can be made to prevent infection by plants, and humans deserves to be considered. The same thing is true for new medications and new vaccines. The reality is that new ways of protecting us will be needed in the future. Gene editing is a tool that we will need, and not just in agriculture. Actually, many of future applications will have a use in human medicine just as much. We must not give scientists a blank cheque about innovation, but we must also be open minded to new ways. Of course, this leads to discussions and all aspects must be considered, and that includes ethics as well.
An example of such discussions, with an unexpected outcome, is the use of gene editing of hens that produce only females. From a technical point of view, this eliminates the issue of chick sexing, as there is no male chick. Male chicks have been an issue in egg production as they would not be useful. The industry used to cull the males but that was cause for ethical issues. So, back to the gene-edited hens. The fact that they produce only females means that, statistically, to produce the same number of females, only half of the mothers are required. This means less feed needed, therefore freeing arable land, therefore less environmental impact. Of course, the ethics of gene technology would be questioned. Surprisingly, the company producing these hens got support from the Compassion in World Farming, which is no small feat. The CIWF is a vocal critic of intensive animal husbandry. The fact that they see an advantage in this application of gene editing is rather interesting and shows that pragmatism is needed if we want to improve for the future.
Bonus number 4: farmers’ ingenuity

If I can think of a profession of people having resilience, adaptability and resourceful beyond the imaginable, I immediately think of farmers. Their work is not just about producing; it is mostly about solving and fixing unexpected problems. Just take a look at what they can do with a roll of duct tape and you know farmers are not your average person. You also know that they innovate with a cost-effective mindset. They perform miracles every day. Here is a device installed by Rose Acre Farms, the second largest egg producer, to deter migrating bird to get close to the hen houses and thus to reduce the risk of contamination with avian flu.
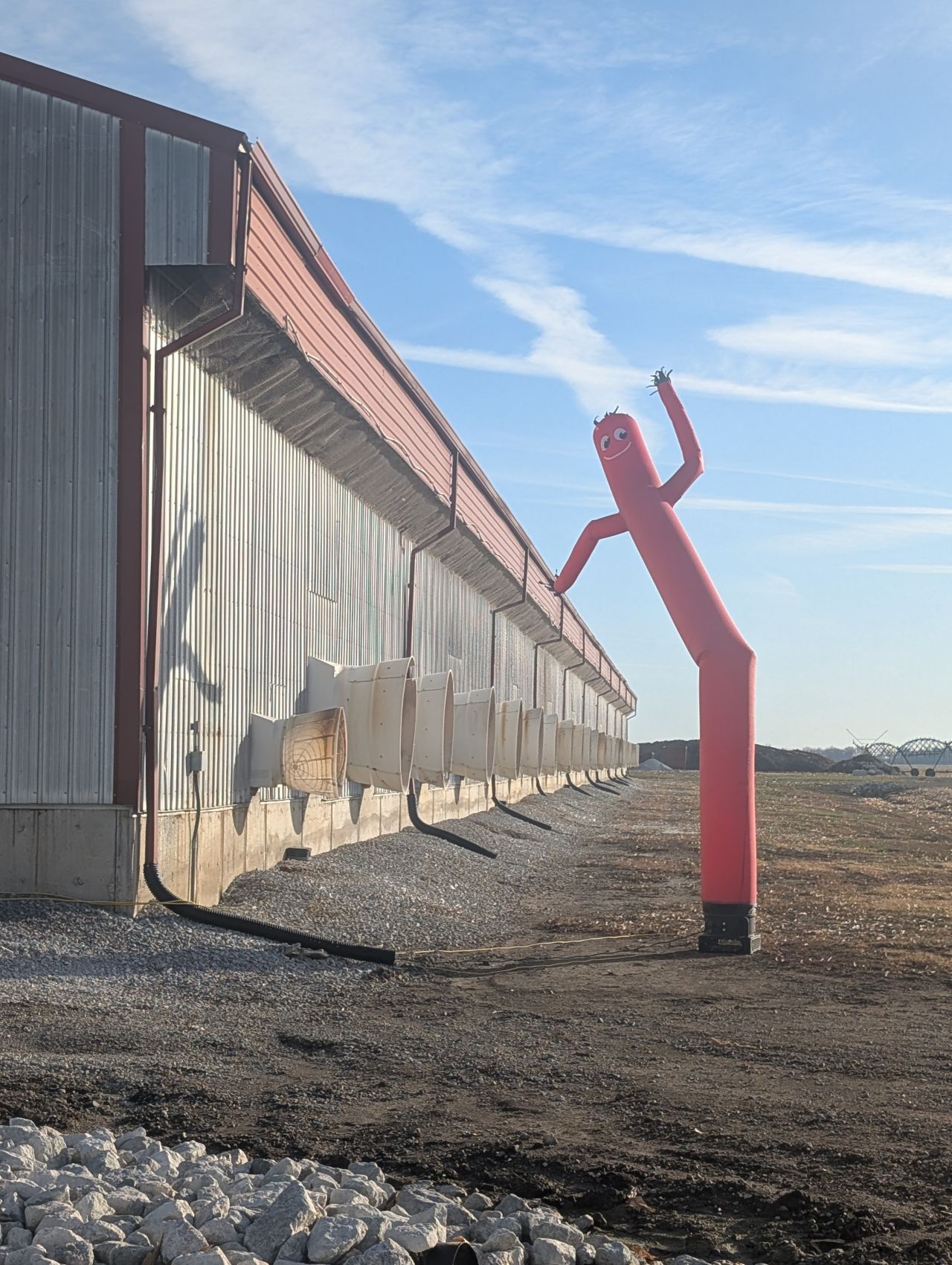

In my previous post in which I discussed the risks of diseases and that AI could be a great help, this shows how ingenuous farmers can be and that innovation is not only about high-tech. I hope for them that this simple device will work. Unfortunately. most consumers do not even realize that and what it takes to produce food. Farmers need more recognition. Even if they sometimes take their time to adopt new methods and technologies, they are definitely always looking at improving their operations and meet the demands from the public and from governments with a dedication that you will not find in many other professions. I regularly lament that farmers are not involved enough in the proper development of innovations. I also lament the fact that farmers are rarely involved and invited in conferences about the future of food and farming. Their practical experience, their knowledge of what works and what does not, of what is possible and what is not are essential contributions for a prosperous future. The world cannot miss their ingenuity.
Next week’s article: The Future of Family Farms: Navigating Generational Changes
Copyright 2025 – Christophe Pelletier – The Food Futurist – The Happy Future Group Consulting Ltd.